Mutatochrom
Mutatochrom ist ein Xanthophyll aus dem Pilz Boletus luridus,[2] Karotten, unreifen Kartoffeln, Maisblättern und der Alge Fucus spiralis.[3][4]
| Strukturformel | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
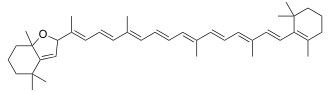 | ||||||||||
| Allgemeines | ||||||||||
| Name | Mutatochrom | |||||||||
| Andere Namen |
| |||||||||
| Summenformel | C40H56O | |||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | ||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 552,872 g·mol−1 | |||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. | ||||||||||
Mutatochrom kommt vermehrt in den Fruchtkörpern der Pilze vor.[2]
Literatur
- R. F. Hunter, R. M. Krakenberger: 1. The oxidation of β-carotene in solution by oxygen. In: Journal of the Chemical Society. 1947, S. 1, doi:10.1039/JR9470000001.
Einzelnachweise
- Dieser Stoff wurde in Bezug auf seine Gefährlichkeit entweder noch nicht eingestuft oder eine verlässliche und zitierfähige Quelle hierzu wurde noch nicht gefunden.
- B. Czeczuga: Investigations on carotenoids in fungi IV. Members of the Boletus genus. In: Qualitas Plantarum. 28, 1978, S. 37–43, doi:10.1007/BF01092999.
- R.J.H. Williams, T.W. Goodwin: The occurrence of mutatochrome in green tissues. In: Phytochemistry. 6, 1967, S. 1037–1039, doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(00)86059-8.
- J. John, H. R. Cama: Metabolism and biological activity of citroxanthin (mutatochrome) in rat. In: International journal for vitamin and nutrition research. Internationale Zeitschrift für Vitamin- und Ernährungsforschung. Journal international de vitaminologie et de nutrition. Band 42, Nummer 2, 1972, S. 278–284, PMID 5053853.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.