Lyssavirus
Lyssavirus ist eine Gattung von Viren, die zu der Familie Rhabdoviridae in der Ordnung Mononegavirales gehört. Ein bekannter Vertreter dieser Gattung ist das Rabiesvirus, welches die Tollwut auslöst.
| Lyssavirus | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
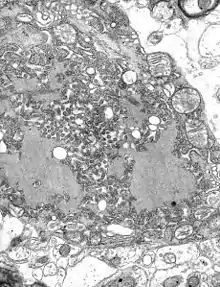
Tollwut-Viren in einer Zelle, Elektronenmikroskop. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Systematik | ||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Taxonomische Merkmale | ||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Wissenschaftlicher Name | ||||||||||||||||||
| Lyssavirus | ||||||||||||||||||
| Links | ||||||||||||||||||
|
Lyssaviren besitzen einzelsträngige RNA mit negativer Polarität als Genom.
Struktur
Lyssaviren haben eine helikale Symmetrie, die Virionen haben eine zylindrische Gestalt. Dies steht im Gegensatz zu anderen Viren, die den Menschen befallen.
Lyssaviren haben eine längliche Gestalt, besitzen eine Virushülle mit so genannten „Spikes“ (Ausstülpungen). Unterhalb der Hülle ist eine Schicht aus Matrixprotein, welche den Kern des Viruspartikels (Virions) aus helikalem Ribonukleoprotein bedeckt.
Genotypen
Lyssaviren werden herkömmlich in insgesamt sieben Genotypen klassifiziert. Diese sieben Genotypen werden in zwei Phylogruppen unterteilt:
- Phylogruppe 1
- Genotyp 1: Rabiesvirus (RABV). Dieses Virus ist das klassische Tollwutvirus.
- Genotyp 4: Duvenhage-Virus (DUVV)
- Genotyp 5: Europäisches Fledermaus-Lyssavirus = European bat lyssavirus (EBLV 1)
- Genotyp 6: Europäisches Fledermaus-Lyssavirus = European bat lyssavirus (EBLV 2)
- Genotyp 7: Australisches Fledermaus-Lyssavirus = Australian bat lyssavirus (ABLV)
- Phylogruppe 2
- Genotyp 2: Lagos-Fledermausvirus = Lagos bat virus (LBV)
- Genotyp 3: Mokola-Virus (MOKV)
Die Gruppe 1 enthält die Genotypen 1, 4, 5, 6, und 7, während die Gruppe 2 die Genotypen 2 und 3 enthält. Ausgenommen Genotyp 2, sind bei allen anderen oben aufgezählten Genotypen Tollwutfälle beim Menschen beschrieben. Zur Analyse wurde das Glykoprotein G genommen, da dieses als Antigen relevant ist. Diese Erkenntnis erklärt auch, wieso Impfstoffe gegen das Rabiesvirus (Typ 1) nicht gegen Viren der Gruppe 2 wirksam sind.[3]
Vier weitere Genotypen wurden beschrieben, dies sind Aravan Virus (1991), Khujand virus (2001), West Caucasian bat lyssavirus (2002), und Irkut virus (2002).[4]
Taxonomie
Die Gattung Lyssavirus besteht nach ICTV mit Stand November 2018 taxonomisch aus den folgenden 16 Spezies:[5]
- Genus Lyssavirus
- Spezies Aravan-Lyssavirus (en. Aravan lyssavirus, früher Aravan Virus, ARAV)
- Spezies Australisches Fledermaus-Lyssavirus (en. Australian bat lyssavirus, ABLV)
- Spezies Bokeloh-Fledermaus-Lyssavirus (en. Bokeloh bat lyssavirus, BBLV)
- Spezies Duvenhage-Virus (en. Duvenhage lyssavirus, DUVV)
- Spezies Europäisches Fledermaus-Lyssavirus 1 (en. European bat 1 lyssavirus, EBLV 1)
- Spezies Europäisches Fledermaus-Lyssavirus 2 (en. European bat 2 lyssavirus, EBLV 2)
- Spezies Gannoruwa-Fledermaus-Lyssavirus (en. Gannoruwa bat lyssavirus, GBLV)
- Spezies Ikoma-Lyssavirus (en. Ikoma lyssavirus, IKOV)
- Spezies Irkut-Lyssavirus (en. Irkut lyssavirus, früher Irkut virus, IRKV)
- Spezies Khujand-Lyssavirus (en. Khujand lyssavirus, früher Khujand virus, KHUV)
- Spezies Lagos-Fledermausvirus (en. Lagos bat lyssavirus, früher Lagos bat virus, LBV)
- Spezies Lleida-Fledermausvirus (en. Lleida bat lyssavirus, LLEBV)
- Spezies Mokola-Virus (en. Mokola lyssavirus, MOKV)
- Spezies Rabiesvirus (en. Rabies lyssavirus, RABV)
- Spezies Shimoni-Fledermausvirus (en. Shimoni bat lyssavirus, SHIBV)
- SpeziesWestkaukasisches Fledermausvirus (en. West Caucasian bat lyssavirus, früher West Caucasian bat lyssavirus, WCBV)
Einzelnachweise
- ICTV Master Species List 2018b.v2. MSL #34, März 2019
- ICTV: ICTV Taxonomy history: Akabane orthobunyavirus, EC 51, Berlin, Germany, July 2019; Email ratification March 2020 (MSL #35)
- Badrane H, Bahloul C, Perrin P, Tordo N: Evidence of two Lyssavirus phylogroups with distinct pathogenicity and immunogenicity. In: J. Virol.. 75, Nr. 7, April 2001, S. 3268–76. doi:10.1128/JVI.75.7.3268-3276.2001. PMID 11238853. PMC 114120 (freier Volltext).
- Kuzmin IV, Hughes GJ, Botvinkin AD, Orciari LA, Rupprecht CE: Phylogenetic relationships of Irkut and West Caucasian bat viruses within the Lyssavirus genus and suggested quantitative criteria based on the N gene sequence for lyssavirus genotype definition. In: Virus Res.. 111, Nr. 1, Juli 2005, S. 28–43. doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2005.03.008. PMID 15896400.
- ICTV: Master Species List 2018a v1, MSL including all taxa updates since the 2017 release. Fall 2018 (MSL #33)