B-Lymphozytenantigen CD20
B-Lymphozytenantigen CD20 ist ein Oberflächenprotein auf der Zelloberfläche von B-Zellen.[1] Es ist phosphoryliert und palmitoyliert. Charakteristisch für CD20, das als Mitglied der MS4A-Familie auch als MS4A1 bekannt ist, sind vier konservierte Transmembrandomänen, die von N- und C-terminalen cytoplasmatischen Domänen flankiert sind. CD20 ist an der humoralen Immunantwort beteiligt. Es bindet an MHCII und reguliert die Aktivierung des B-Zell-Rezeptors. Die Antikörper Rituximab,[2] Obinutuzumab, Ocrelizumab und Ofatumumab binden an CD20.
| B-lymphocyte antigen CD20 | ||
|---|---|---|
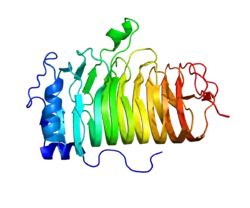 | ||
| nach PDB 1S8B | ||
| Andere Namen |
B-lymphocyte surface antigen B1, Bp35, Leukocyte surface antigen Leu-16, Membrane-spanning 4-domains subfamily A member 1 | |
| Eigenschaften des menschlichen Proteins | ||
| Masse/Länge Primärstruktur | 297 Aminosäuren, 33.077 Da | |
| Bezeichner | ||
| Externe IDs | ||
Weblinks
Einzelnachweise
- T. F. Tedder, M. Streuli, S. F. Schlossman, H. Saito: Isolation and structure of a cDNA encoding the B1 (CD20) cell-surface antigen of human B lymphocytes. In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Band 85, Nummer 1, Januar 1988, S. 208–212, PMID 2448768, PMC 279513 (freier Volltext).
- M. S. Cragg, C. A. Walshe, A. O. Ivanov, M. J. Glennie: The biology of CD20 and its potential as a target for mAb therapy. In: Current directions in autoimmunity. Band 8, 2005, S. 140–174, doi:10.1159/000082102, PMID 15564720.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.