AP-1
AP-1 ist ein Transkriptionsfaktor. AP-1 ist ein heterodimerer Proteinkomplex aus Proteinen der Familien ATF, JDP, c-Fos und c-Jun und bindet als Dimer an DNA, um die Transkription bestimmter Gene einzuleiten.
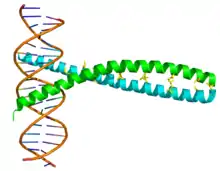
AP-1 im Komplex mit DNA (braun), mit AP-1 aus c-Fos (cyan) und c-Jun (grün) bestehend
Eigenschaften
Die von AP-1 regulierten Gene umfassen Gene der Zelldifferenzierung, der Zellteilung und der Apoptose.[1] Die Genexpression des AP-1 selbst wird durch Zytokine, Wachstumsfaktoren, Infektionen und Stressfaktoren induziert.[2] AP-1 bindet an die DNA über basische Aminosäuren, während die Dimerisierung durch einen Leucin-Zipper vermittelt wird.[3] AP-1 verstärkt die Genexpression am 12-O-Tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate DNA response element (TRE, Sequenz 5'-TGAG/CTCA-3').[2]
Einzelnachweise
- Ameyar M, Wisniewska M, Weitzman JB: A role for AP-1 in apoptosis: the case for and against. In: Biochimie. 85, Nr. 8, August 2003, S. 747–52. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2003.09.006. PMID 14585541.
- Hess J, Angel P, Schorpp-Kistner M: AP-1 subunits: quarrel and harmony among siblings. In: J. Cell. Sci.. 117, Nr. Pt 25, 2004, S. 5965–73. doi:10.1242/jcs.01589. PMID 15564374.
- Glover JN, Harrison SC: Crystal structure of the heterodimeric bZIP transcription factor c-Fos-c-Jun bound to DNA. In: Nature. 373, Nr. 6511, 1995, S. 257–61. doi:10.1038/373257a0. PMID 7816143.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.