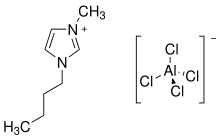
1-Butyl-3-methylimidazoliumtetrachloroaluminat
1-Butyl-3-methylimidazoliumtetrachloroaluminat ist eine ionische Flüssigkeit (auch: ionic liquid oder Flüssigsalz), also ein Salz, dessen Schmelzpunkt unter 100 °C liegt.
| Strukturformel | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | |||||||||||||||||||
| Name | 1-Butyl-3-methylimidazoliumtetrachloroaluminat | ||||||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C8H15Cl4N2Al | ||||||||||||||||||
| Kurzbeschreibung | |||||||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 308,01 g·mol−1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand |
flüssig | ||||||||||||||||||
| Dichte |
1,2533 g·cm−3 (bei 5,1 °C)[3] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. | |||||||||||||||||||
Darstellung
1-Butyl-3-methylimidazoliumtetrachloroaluminat kann durch Mischen von 1-Butyl-3-methylimidazoliumchlorid mit Aluminiumchlorid dargestellt werden. Die erste Synthese gelang John S. Wilkes 1981.[1] In der ionischen Flüssigkeit liegt ein Gleichgewicht zwischen verschiedenen Aluminium-Spezies vor, welches durch die Menge an eingesetztem AlCl3 während der Synthese beeinflusst werden kann:
Verwendung
1-Butyl-3-methylimidazoliumtetrachloroaluminat kann in der extraktiven Entschwefelung von Kraftstoffen[4][2], als Elektrolyt für Dual-Ionen-Batterien[5] und als Reaktionsmedium[6] verwendet werden.
Sicherheitshinweise
Die Substanz reagiert mit Wasser und setzt dabei unter anderem Chlorwasserstoff frei.
Einzelnachweise
- John S. Wilkes, Joseph A. Levisky, Robert A. Wilson, Charles L. Hussey: Dialkylimidazolium chloroaluminate melts: a new class of room-temperature ionic liquids for electrochemistry, spectroscopy and synthesis. In: Inorganic Chemistry. Band 21, Nr. 3, März 1982, ISSN 0020-1669, S. 1263–1264, doi:10.1021/ic00133a078.
- Roland Schmidt: [bmim]AlCl4 Ionic Liquid for Deep Desulfurization of Real Fuels. In: Energy & Fuels. Band 22, Nr. 3, Mai 2008, ISSN 0887-0624, S. 1774–1778, doi:10.1021/ef7007216.
- Datenblatt 1-Butyl-3-methyl-imidazolium-tetrachloroaluminat bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 23. Februar 2022 (PDF).
- Hongping Li, Yonghui Chang, Wenshuai Zhu, Wei Jiang, Ming Zhang: A DFT Study of the Extractive Desulfurization Mechanism by [BMIM] + [AlCl 4 ] − Ionic Liquid. In: The Journal of Physical Chemistry B. Band 119, Nr. 19, 14. Mai 2015, ISSN 1520-6106, S. 5995–6009, doi:10.1021/acs.jpcb.5b00516.
- Surya Sekhar Manna, Preeti Bhauriyal, Biswarup Pathak: Identifying suitable ionic liquid electrolytes for Al dual-ion batteries: role of electrochemical window, conductivity and voltage. In: Materials Advances. Band 1, Nr. 5, 2020, ISSN 2633-5409, S. 1354–1363, doi:10.1039/D0MA00292E.
- Jhillu S. Yadav, Basi V. S. Reddy, Maddi Sridhar Reddy, Namelikonda Niranjan, Attaluri R. Prasad: Lewis Acidic Chloroaluminate Ionic Liquids: Novel Reaction Media for the Synthesis of 4-Chloropyrans. In: European Journal of Organic Chemistry. Band 2003, Nr. 9, Mai 2003, S. 1779–1783, doi:10.1002/ejoc.200210638.