Secoiridoide
Secoiridoide sind Spezialformen der Iridoide. Sie unterscheiden sich durch eine Spaltung des Cyclopentanringes, was ihnen nur einen heterocyclischen Sechsring überlässt. Die Spaltung kann zur Weitersynthese gebraucht werden, sodass zwei Sechsringe entstehen. Die Stammverbindung der Secoiridoide ist das Secologanin, das eine Schlüsselverbindung in der Biosynthese der meisten Indol-Alkaloide, der China-, Ipecacuanha- und Pyrrolochinolin-Alkaloide sowie einfacher Monoterpen-Alkaloide ist.[1]
| Trivialname | Summenformel | relative Molmasse (Mr) | Schmelzpunkt | Spezifischer Drehwinkel [α]D in °·ml·dm−1·g−1 (Lösungsmittel) | CAS-Nummer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Secologanin (Lonicerosid) | C17H24O10 | 388,37 | amorph | −105 (Methanol) | 19351-63-4 |
| Secologaninsäure | C16H22O10 | 374,34 | amorph | 60077-46-5 | |
| Vogelosid | C17H24O10 | 388,37 | amorph | 60077-47-6 | |
| Swerosid | C16H22O9 | 358,35 | amorph | −236 (Wasser) | 14215-86-2 |
| Swertiamarin (Swertiamarosid) | C16H22O10 | 374,34 | 113–114 °C | −127 (Ethanol) | 17388-39-5 |
| Eustomosid | C16H22O11 | 390,34 | amorph | −123 (Methanol) | 74213-75-5 |
| Eustomorussid | C16H24O12 | 408,36 | amorph | −73 (Methanol) | 74213-77-7 |
| Secoxyloganin | C17H24O11 | 404,37 | 58822-47-2 |
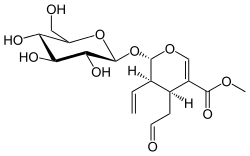
Secologanin, die Stammverbindung der Secoiridoide

Oleuropein, ein glykosiliertes Secoiridoid
Einzelnachweise
- Eintrag zu Secoiridoide. In: Römpp Online. Georg Thieme Verlag, abgerufen am 10. Juni 2015.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.