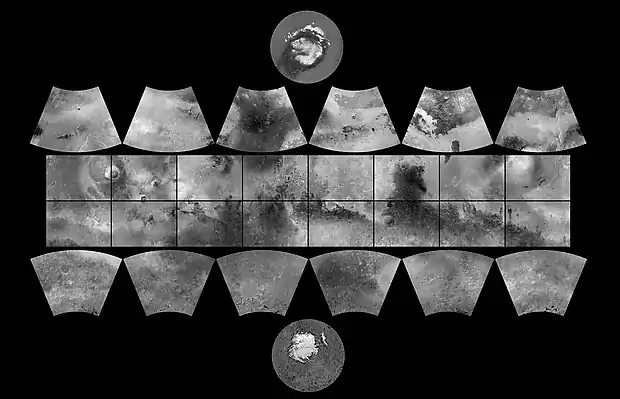
Mare Australe (Gradfeld)
Das Mare-Australe-Gradfeld gehört zu den 30 Gradfeldern des Mars. Sie wurden durch die United States Geological Survey (USGS) festgelegt. Die Nummer ist MC-30, das Gradfeld umfasst das Gebiet von 0° bis 360° westlicher Länge und von −90° bis −65° südlicher Breite.[1][2]
Das Gradfeld bedeckt den Südpol inklusive der Eiskappen. Der Name kommt von einem Albedo feature im Planum Australe, eine den Südpol umgebende Eiskappe.[3] Der Mars Polar Lander zerschellte in dieser Region.[4][5]
Andere Gradfelder
Weblinks
Commons: Mare Australe – Sammlung von Bildern, Videos und Audiodateien
Einzelnachweise
- M.E. Davies, R.M. Batson, S.S.C. Wu: Geodesy and Cartography. In: H.H. Kieffer, B.M. Jakosky, C.W. Snyder, M.S. Matthews (Hrsg.): Mars. University of Arizona Press, Tucson 1992, ISBN 978-0-8165-1257-7.
- Mare Australe im Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature der IAU (WGPSN) / USGS
- Patrick Moore and Robin Rees, ed. Patrick Moore's Data Book of Astronomy (Cambridge University Press, 2011), p. 130.
- Mars Polar Lander Official Website. In: mars.nasa.gov. Abgerufen am 8. November 2016.
- NASA Reveals Probable Cause of Mars Polar Lander and Deep Space-2 Mission Failures. | SpaceRef – Your Space Reference. In: www.spaceref.com. Abgerufen am 8. November 2016.
- Oliver Morton: Mapping Mars: Science, Imagination, and the Birth of a World. Picador USA, New York 2002, ISBN 0-312-24551-3, S. 98.
- PIA03467: The MGS MOC Wide Angle Map of Mars photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov, 16. Februar 2002
- Davies, M.E.; Batson, R.M.; Wu, S.S.C. "Geodesy and Cartography" in Kieffer, H.H.; Jakosky, B.M.; Snyder, C.W.; Matthews, M.S., Eds. Mars. University of Arizona Press: Tucson, 1992.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.