Dehydrocyclisierung
Unter Dehydrocyclisierung versteht man die katalytische Bildung von Aromaten aus Alkanen unter Freisetzung von Wasserstoff, etwa beim katalytischen Reforming.
Reaktion
Die katalytische Bildung von Toluol aus Heptan läuft an zwei verschiedenen katalytischen Zentren an. An den Säurezentren läuft bevorzugt die Cyclisierung ab, an den Metallzentren die Dehydrierungsreaktionen.[1]
Cyclisierung von n-Heptan zu Methylcyclohexan bzw. 1,2-Dimethylcyclopentan:
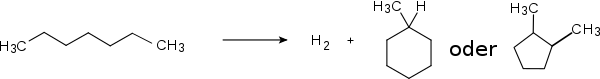
Dehydrierung von Methylcyclohexan zu Toluol:
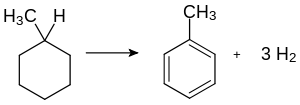
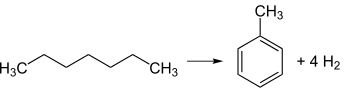
Die Gesamtreaktion der Cyclisierung von n-Heptan zu Toluol läuft wie folgt ab:
Einzelnachweise
- CCR Platforming (Memento vom 28. Mai 2008 im Internet Archive)
Weblinks
- Eintrag zu catalytic dehydrocyclization. In: IUPAC (Hrsg.): Compendium of Chemical Terminology. The “Gold Book”. doi:10.1351/goldbook.C00891 – Version: 2.3.3.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.