Biliverdin-Reduktase
Die Biliverdin-Reduktase (BVR) ist ein Enzym des Häm-Abbaus in Tieren, es katalysiert die Reduktion von Biliverdin zu Bilirubin. Beim Menschen sind zwei paraloge Isoformen bekannt: BVR-A ist hauptsächlich in der Leber zu finden und BVR-B wird ausschließlich im Embryo exprimiert. Man vermutet, dass BVR-A weitere Funktionen im Zellkern ausübt, da es zur Autophosphorylierung und zur Bindung an DNA in der Lage ist. BVR-B kann außerdem Flavine reduzieren.[2][3]
| Biliverdin-Reduktase | ||
|---|---|---|
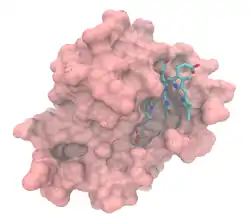 | ||
| Oberflächenmodell der BVR-B mit NADP und Biliverdin als Stäbchen nach PDB 1HE2 | ||
|
Vorhandene Strukturdaten: 2H63 | ||
| Masse/Länge Primärstruktur | 296 / 206 Aminosäuren | |
| Sekundär- bis Quartärstruktur | Monomer | |
| Kofaktor | Zn2+ | |
| Bezeichner | ||
| Gen-Name(n) | BLVRA, BLVRB | |
| Enzymklassifikation | ||
| EC, Kategorie | 1.3.1.24, Oxidoreduktase | |
| Reaktionsart | Redoxreaktion | |
| Substrat | Biliverdin + NADPH/H+ | |
| Produkte | Bilirubin + NADP+ | |
| Vorkommen | ||
| Übergeordnetes Taxon | mehrzellige Tiere[1] | |
Katalysierte Reaktion
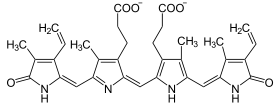 + NADPH/H+ →
+ NADPH/H+ → 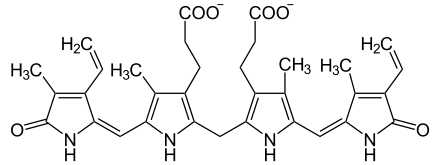 + NADP+
+ NADP+
Biliverdin wird zu Bilirubin reduziert. BVR-A ist das einzige bekannte Enzym mit einem doppelten Aktivitätsprofil in Abhängigkeit von pH und Cofaktor (NADPH bei pH 8,7 und NADH bei pH 7,0).[3]
Einzelnachweise
- InterPro-Eintrag
- UniProt P53004
- Tudor C, Lerner-Marmarosh N, Engelborghs Y, Gibbs PE, Maines MD: Biliverdin reductase is a transporter of haem into the nucleus and is essential for regulation of HO-1 gene expression by haematin. In: Biochem. J.. 413, Nr. 3, August 2008, S. 405–16. doi:10.1042/BJ20080018. PMID 18412543. PMC 2723824 (freier Volltext).
Weblinks
Wikibooks: Biochemie und Pathobiochemie: Porphyrinabbau – Lern- und Lehrmaterialien
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.