Balsohn-Alkylierung
Die Balsohn-Alkylierung ist eine Namensreaktion der organischen Chemie, welche 1879 von M. Balsohn veröffentlicht wurde.[1]
Übersichtsreaktion
Bei der Balson-Alkylierung reagiert Benzol in Anwesenheit von Aluminiumchlorid mit Ethen zu Ethylbenzol.[1]
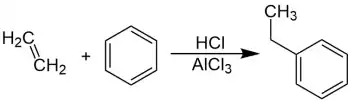
Reaktionsmechanismus
Im vorgeschlagenen Reaktionsmechanismus reagiert das Ethen zunächst mit dem Aluminiumchlorid zu einem Carbeniumion. Das Carbeniumion wird anschließend nukleophil vom aromatischen Ring des Benzols angegriffen. Nachdem ein Proton abgespalten wurde entsteht das gewünschte Ethylbenzol.[1][2]

Modifikation
Neben Aluminiumchlorid lassen sich auch Schwefelsäure[3], Phosphorsäure[4], Phosphorpentoxid[1] und Borontrifluorid[5] zur Aktivierung verwenden. Außerdem ist die Reaktion nicht auf Ethen und Benzol beschränkt, auch andere Alkene und Aromaten lassen sich in der Balson-Alkylierung umsetzen.[6][7][8] Dabei folgt die Alkylierung der para/ortho-Regioselektivität.[1]
Anwendung
Die Balson-Alkylierungen wurde bereits für industrielle Produktionen angewandt.[9]
Einzelnachweise
- Zerong Wang: Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, NJ, USA 2010, ISBN 978-0-470-63885-9, doi:10.1002/9780470638859.
- Ernest M. Hodnett, Charles F. Feldman: Kinetics of the Friedel-Crafts Ethylation of Benzene with Ethylene and with Ethylene-C14. In: Journal of the American Chemical Society. Band 81, Nr. 7, 1. April 1959, S. 1638–1640, doi:10.1021/ja01516a032.
- V. N. Ipatieff, B. B. Corson, Herman Pines: Influence of Sulfuric Acid Concentration upon Reaction between Olefins and Benzene. In: Journal of the American Chemical Society. Band 58, Nr. 6, 1. Juni 1936, S. 919–922, doi:10.1021/ja01297a021.
- V. N. Ipatieff, Herman Pines, V. I. Komarewsky: Phosphoric Acid as the Catalyst for Alkylation of Aromatic Hydrocarbons. In: Industrial & Engineering Chemistry. Band 28, Nr. 2, 1. Februar 1936, S. 222–223, doi:10.1021/ie50314a019.
- Vladimir N. Ipatieff, Aristid V. Grosse: Reaction of Paraffins with Olefins1. In: Journal of the American Chemical Society. Band 57, Nr. 9, 1. September 1935, S. 1616–1621, doi:10.1021/ja01312a034.
- Henry Gilman, Nathaniel O. Calloway, Robert R. Burtner: Orientation in the Furan Series. IX. The Friedel—Crafts Reaction with 2-Furfural. In: Journal of the American Chemical Society. Band 57, Nr. 5, 1. Mai 1935, S. 906–907, doi:10.1021/ja01308a037.
- J. W. Cook, E. C. Dodds, C. L. Hewett: A Synthetic Oestrus-Exciting Compound. In: Nature. Band 131, Nr. 3298, 1933, S. 56–57, doi:10.1038/131056b0.
- Joseph B. Niederl, Charles H. Riley: The Addition of Phenols to Arylenes. The Synthesis of Phenylthymol and its Isomers. In: Journal of the American Chemical Society. Band 56, Nr. 11, 1. November 1934, S. 2412–2414, doi:10.1021/ja01326a059.
- Patent US5068479A: Preparation of 1,1,3,4,4,6-hexamethyl-1,2,3,4-tetra-hydronaphthalene. Angemeldet am 13. März 1991, veröffentlicht am 26. November 1991, Anmelder: BASF SE, Erfinder: Michael Huellmann, Herbert Mayr, Rainer Becker.