Polychlorierte Phenoxyphenole
Die polychlorierten Phenoxyphenole (PCPP) sind eine Gruppe organischer polyhalogenierter Verbindungen. Darunter finden sich Triclosan [5-Chlor-2-(2,4-dichlorphenoxy)phenol] und Predioxin [2,3,4-Trichlor-6-(2,4-dichlorphenoxy)phenol].
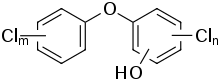
Allgemeine Struktur von PCPP
Im Triclosan können Spuren von Dioxinen und Furanen enthalten sein,[1] Predioxin hingegen wird zu Dioxinen abgebaut.
Bemerkenswert ist, dass die Dioxine, welche durch wässrige Photolyse von Triclosan entstehen, als nicht-toxisch eingestuft wurden.[2][3]
Einzelnachweise
- K. L. Rule, V. R. Ebbett, P. J. Vikesland: Formation of chloroform and chlorinated organics by free-chlorine-mediated oxidation of triclosan. In: Environmental Science & Technology. 39, Nr. 9, 2005, S. 3176–3185. doi:10.1021/es048943+. PMID 15926568.
- Douglas E. Latch, Jennifer L. Packer, William A. Arnold, Kristopher McNeill: Photochemical conversion of triclosan to 2,8-dichlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in aqueous solution. In: Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry. 158, 2003, S. 63. doi:10.1016/S1010-6030(03)00103-5.
- Joseph D. Wisk, Keith R. Cooper: Comparison of the toxicity of several polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzofuran in embryos of the Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). In: Chemosphere. 20, Nr. 3–4, 1990, S. 361. doi:10.1016/0045-6535(90)90067-4.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.