Nukleosid-Antibiotika
Die Nukleosid-Antibiotika sind eine Gruppe von Antibiotika, welche sich von Nukleosiden ableiten. Sie werden in der Humanmedizin nicht verwendet.
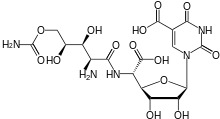
Polyoxin D

Puromycin
Die Nukleosid-Antibiotika weisen eine ähnliche Struktur auf, unterscheiden sich aber in ihren Wirkmechanismen. Die antibakteriellen Nukleosid-Antibiotika hemmen die Biosynthese der Zellwand durch Inhibierung der bakteriellen Translokase I (MraY). Die fungiziden Nukleosid-Antibiotika wirken auch auf die Zellwand, allerdings hemmen sie die Chitin-Synthase. Die antiviralen Nukleosid-Antibiotika blockieren die Peptidyltransferase.
Einteilung
- Antibakterielle (Uridin-)Antibiotika
- Uridyl-Peptid-Antibiotika
- Pacidamycin
- Napsamycin
- Mureidomycin
- Sansanmycin
- Uridyl-Lipopeptid-Antibiotika
- Liposidomycin
- Caprazamycin
- Muraymycin
- Muraminomicin
- Uridyl-Lipodisaccharid-Antibiotika
- Tunicamycin
- Uridyl-Glycosylpeptid-Antibiotika
- Capuramycin
- Fungizide Nukleosid-Antibiotika
- Nikkomycin
- Polyoxine
- Blasticidin S
- Arginomycin
- Mildiomycin
- Antivirale Nukleosid-Antibiotika
- Puromycin (leitet sich vom Adenosin ab)
Literatur
- Michael Winn, Rebecca J. M. Goss, Ken-ichi Kimura, Timothy D. H. Bugg: Antimicrobial nucleoside antibiotics targeting cell wall assembly: Recent advances in structure–function studies and nucleoside biosynthesis. In: Natural Product Reports. Band 27, Nr. 2, 2010, S. 279, doi:10.1039/b816215h.
- Guoqing Niu, Huarong Tan: Nucleoside antibiotics: biosynthesis, regulation, and biotechnology. In: Trends in Microbiology. 2014, doi:10.1016/j.tim.2014.10.007.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.