Mahasim
Mahasim[6] ist ein etwa 170 Lichtjahre entfernter Ap-Stern im Sternbild Fuhrmann mit einer scheinbaren Helligkeit von rund 2,7 mag. In einer Entfernung von knapp 4 Bogensekunden liegt ein Begleitstern der Spektralklasse F2-5 V mit einer scheinbaren Helligkeit von 7,2 mag.[3]
| Doppelstern Mahasim (θ Aurigae) | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| AladinLite | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Beobachtungsdaten Äquinoktium: J2000.0, Epoche: J2000.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||
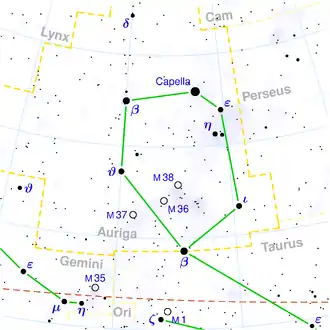
| Sternbild | Fuhrmann | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Rektaszension | 05h 59m 43,27s [1] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Deklination | +37° 12′ 45,3″ [1] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Helligkeiten | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Scheinbare Helligkeit | 2.62 bis 2.70 mag | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Spektrum und Indices | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Veränderlicher Sterntyp | ACV[2] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| B−V-Farbindex | (−0.08) [1] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| U−B-Farbindex | (−0.18) [1] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| R−I-Index | (−0.06) [1] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Spektralklasse | A0pSi / F2-5 V [3] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Astrometrie | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Radialgeschwindigkeit | (29.3 ± 1.7) km/s [1] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Parallaxe | (19.70 ± 0.16) mas | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Entfernung | (165 ± 2) Lj (51) pc | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Eigenbewegung [1] | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Rek.-Anteil: | (43.63 ± 0.21) mas/a | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Dekl.-Anteil: | (−73.79 ± 0.08) mas/a | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Physikalische Eigenschaften | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Radius | (5.1 ± 0.4) R☉ [4] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Effektive Temperatur | (10400 ± 300) K [4] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotationsdauer | 3.62 d [5][2] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Andere Bezeichnungen und Katalogeinträge | |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
Der Stern trägt auch den historischen Eigennamen Bogardus sowie – in der traditionellen chinesischen Astronomie – 五車四.
Quellen
- Adelman, S. J.; Hensberge, H.; van Rensbergen, W.: General study of the apparently average magnetic Ap star theta Aurigae. I. Data and method; in: Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series (ISSN 0365-0138), Vol. 57, S. 121ff. (Juli 1984), bibcode:1984A&AS...57..121A
Einzelnachweise
- tet Aur. In: SIMBAD. Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg, abgerufen am 8. September 2018.
- tet Aur. In: VSX. AAVSO, abgerufen am 8. September 2018.
- C. Schröder, J. H. M. M. Schmitt: X-ray emission from A-type stars. In: Astronomy and Astrophysics. 475, Nr. 2, November 2007, S. 677–684. bibcode:2007A&A...475..677S. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20077429.
- D. Shulyak, G. Valyavin, O. Kochukhov, B.-C. Lee, G. Galazutdinov, K.-M. Kim, I. Han, T. Burlakova, V. Tsymbal: The Lorentz force in atmospheres of CP stars: θ Aurigae. In: Astronomy & Astrophysics. 464, Nr. 3, März 2007, S. 1089–1099. arxiv:astro-ph/0612301. bibcode:2007A&A...464.1089S. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20064998.
- J. B. Rice, D. E. Holmgren, D. A. Bohlender: The distribution of oxygen on the surface of the Ap star θ Aur. An abundance Doppler image to compare with ɛ UMa. In: Astronomy and Astrophysics. 424, September 2004, S. 237–244. bibcode:2004A&A...424..237R. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20035639.
- von der IAU verifizierte Liste mit dem Namen
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.