Kartoffel-Dextrose-Agar
Kartoffel-Dextrose-Agar (PDA von englisch Potato dextrose agar) ist ein verbreiteter Nährboden zur Kultivierung von Hefen und Schimmelpilzen.[1]
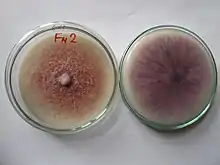
Pilz der Gattung Fusarium aus Erde auf Kartoffel-Dextrose-Agar angezüchtet
Eine beispielhafte Zusammensetzung sind 4 g/l Kartoffelstärke, 20 g/l Glucose und 15 g/l Agar.[2] Das Bakterienwachstum wird entweder durch Ansäuern mit Weinsäure bis zu einem pH-Wert von 3,5 oder durch Zugabe von Antibiotika (Chloramphenicol oder Chlortetracyclin) unterdrückt.[1]
Einzelnachweise
- Sagar Aryal: Potato Dextrose Agar (PDA)- Principle, Uses, Composition, Procedure and Colony Characteristics. In: Online Microbiology Notes. 7. Juli 2015, abgerufen am 17. Oktober 2016.
- Kartoffel-Extrakt-Glucose Agar
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.