Jensen-Reaktion
Die Jensen-Reaktion, auch Jensen-Acylierung, ist eine Namensreaktion aus der Organischen Chemie. Die Reaktion ist nach ihrem Entdecker Bror Skytte Jensen benannt.[1] Sie dient zur Darstellung von 4-Acyl-5-pyrazolonen/4-Acylpyrazol-5-olen (3, vgl. Abbildung) bzw. 4-Acyl-5-isoxazolonen aus Pyrazolonen (1) bzw. aus Isoxazolonen und Carbonsäurechloriden (2) in Gegenwart von Calciumhydroxid Ca(OH)2. Das bevorzugte Lösungsmittel ist 1,4-Dioxan.
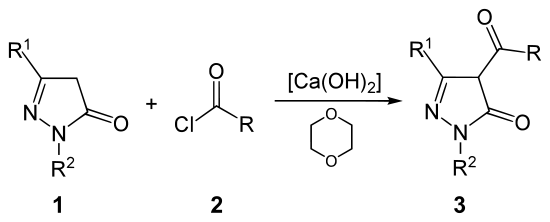
Reaktionsschema der Jensen-Reaktion
Einzelnachweise
- Bror Skytte Jensen: The synthesis of 1-phenyl-3-methyl-4-acyl-pyrazolones-5. In: Acta Chem. Scand. Band 13, Nr. 8, 1959, S. 1668–1670 (actachemscand.org [PDF; abgerufen am 8. Juni 2015]).
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.