Frobisher-Bucht
Die Frobisher-Bucht (englisch Frobisher Bay) ist ein Meeresarm der Labradorsee, der von Südosten aus etwa 230 km in die Baffininsel in Nunavut im Nordosten Kanadas hineinreicht.[1]
| Frobisher-Bucht Frobisher Bay | ||
|---|---|---|
| Gewässer | Labradorsee (Atlantischer Ozean) | |
| Landmasse | Baffin Island | |
| Geographische Lage | 62° 50′ N, 66° 35′ W | |
| ||
| Breite | max. 40 km | |
| Länge | 230 km | |
| Inseln | Chase Island, Gabriel Island, Bruce Island, Fletcher Island, Pike Island, Augustus Island u. a. | |
| Zuflüsse | Armshaw River, Sylvia Grinnell River | |
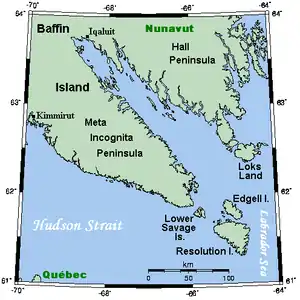 Die Frobisher-Bucht zwischen den Halbinseln Meta-Incognita und Hall Die Frobisher-Bucht zwischen den Halbinseln Meta-Incognita und Hall | ||
Sie ist umschlossen von den beiden Halbinseln Meta-Incognita (im Südwesten) und Hall (im Nordosten). In ihrem Inneren liegt der Küstenort Iqaluit (früher Frobisher Bay).
Nahe dieser Bucht befinden sich Loks Island, Edgell Island und Resolution Island.
Die Frobisher-Bucht wurde 1576 von Martin Frobisher entdeckt. Dieser ging damals jedoch irrtümlicherweise aufgrund der Zeno-Karte davon aus, sich vor der Küste Grönlands zu befinden.[2]
Weblinks
Commons: Frobisher-Bucht – Sammlung von Bildern, Videos und Audiodateien
Einzelnachweise
- Frobisher Bay in The Canadian Encyclopedia (englisch)
- William J. Mills: Exploring Polar Frontiers: A Historical Encyclopedia. ABC-Clio, Santa Barbara 2003, S. 247, ISBN 978-1576074220.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.