Emmert-Reaktion
Die Emmert-Reaktion ist eine Namensreaktion aus dem Bereich der organischen Chemie. Diese Reaktion wurde ursprünglich von den Chemikern Bruno Emmert und Erich Asendorf im Jahre 1939 beschrieben und dient zur Herstellung von 2-Pyridin-dialkylcarbinol.[1]
Übersichtsreaktion
Die Emmert-Reaktion dient der Herstellung von 2-Pyridin-dialkylcarbinol 3, durch die Umsetzung von Pyridin 1 und einem Keton 2 in Gegenwart von Aluminium- oder Magnesium-Amalgam.[2][3]
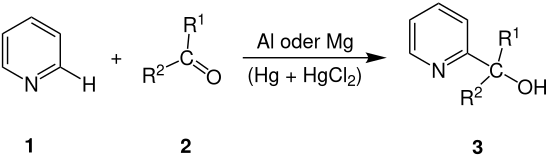
Emmert-Reaktion Reaktionsschema
Einzelnachweise
- B. Emmert und E. Asendorf: Eine Synthese von α‐Pyridyl‐dialkyl‐carbinolen, E., Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft, 1939, 72, 1188, doi: 10.1002/cber.19390720610.
- (a) Sheinkman, A. K.; Nelin, E. N.; Luk’yanenko, L. V. und Klyuev, N. A., Zh. Org. Khim., 1978, 14, 2542.
(b) Tschesche, R. and Fuehrer, W., Chem. Ber., 1978, 111, 3502.
(c) Sheinkman, A. K.; Potashnikova, S. G. und Baranov, S. N., Zh. Org. Khim., 1971, 7, 1550.
(d) Russell, C. A.; Crawforth, C. E. und Meth-Cohn, O., J. Chem. Soc. D, 1970, 1406.
(e) Bachman, G. B.; Hamer, M.; Dunning, E. und Schisla, R. M.: Heterogeneous Bimolecular Reduction. I. General Considerations of Mechanism. The Emmert Reaction, J. Org. Chem., 1957, 22, 1296–1302, doi:10.1021/jo01362a003.
(f) Lochte, H. L.; Kruse, P. F. and Wheeler, E. N.: The Emmert Reaction in the Synthesis of Alkyl- and Cycloalkylpyridines, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1953, 75, 4477–4481, doi:10.1021/ja01114a024. - Zerong Wang: Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, NJ, USA 2010, ISBN 978-0-470-63885-9, S. 993, doi:10.1002/9780470638859 (wiley.com).
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.