Diamidophosphate
Diamidophosphate sind eine Gruppe chemischer Verbindungen. Es handelt sich um die Salze und Ester der Diamidophosphorsäure (CAS-Nr. 10043-91-1). Das Anion wird als Diamidophosphat, kurz DAP, bezeichnet, ist eine organische Phosphat-Aminoverbindung und zählt zu den Phosphoramidaten.
| Diamidophosphorsäure und deren Derivate |
|---|
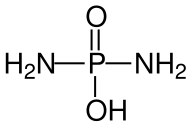
Diamidophosphorsäure |
 Diamidophosphor- säureanion |
 Diamidophosphor- säurenatriumsalz CAS-Nr. 17097-14-2 |
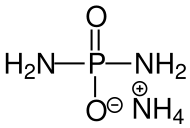 Diamidophosphor- säureammoniumsalz CAS-Nr. 13597-81-4 |
Wirkung und Bedeutung
DAP ist wegen seiner Ähnlichkeit zu Diamidohydrogenorthocarbonat ein effektiver Inhibitor der Urease (Übergangszustandanalogon).[1]
DAP wurde als mögliches, phosphorylierendes Agenz in der präbiotischen Evolution erster organischer Verbindungen und Vorläufermolekülen irdischen Lebens wie Peptide, Lipide oder Nukleotide in Verbindung gebracht.[2]
Weblinks
- Jan Osterkamp: Präbiotische Evolution: Kickstarter des Lebens in der Ursuppe. In: spektrum.de. 6. November 2017, abgerufen am 7. November 2017.
Einzelnachweise
- Sonja Herres-Pawlis, Peter Klüfers: Bioanorganische Chemie: Metalloproteine, Methoden und Modelle. John Wiley & Sons, 2017, ISBN 978-3-527-67549-4, S. 18 (eingeschränkte Vorschau in der Google-Buchsuche).
- Clémentine Gibard et al.: Phosphorylation, oligomerization and self-assembly in water under potential prebiotic conditions. In: Nature Chemistry. 2017, doi:10.1038/nchem.2878.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.