Soai-Reaktion
Die Soai-Reaktion ist eine Alkylierungs-Reaktion von Pyrimidin-5-carbaldehyd mit Diisopropylzink. Das dabei entstehende Produkt – ein Pyrimidylalkohol – wirkt dabei als ein Autokatalysator: Bei Verwendung geringer Mengen des gleichen Katalysators mit niedrigem Enantiomerenüberschuss (ee) entsteht ein Produkt mit hohem ee-Wert.[1] Beginnend mit einem Pyrimidylalkohol, mit extrem niedrigem ee von ca. 0,00005 %, erhält man in drei Autokatalysecyclen ein Produkt mit > 99,5 % ee, eine Steigerung um den Faktor von ca. 630.000.
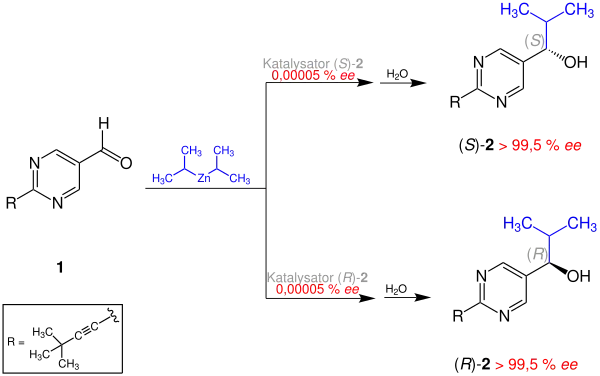 Soai-Reactie mit asymmetrischer Autokatalyse und Erhöhung des ee
Soai-Reactie mit asymmetrischer Autokatalyse und Erhöhung des ee
Der japanische Chemiker Kensō Soai (* 1950) entdeckte diese Reaktion 1995.[2]
Siehe auch
Einzelnachweise
- Chirality and Life: A Short Introduction to the Early Phases of Chemical Evolution, S. 16–17.
- Takanori Shibata, Hiroshi Morioka, Tadakatsu Hayase, Kaori Choji, Kenso Soai: Highly Enantioselective Catalytic Asymmetric Automultiplication of Chiral Pyrimidyl Alcohol. In: Journal of the American Chemical Society. 118, 1996, S. 471. doi:10.1021/ja953066g.
Weitere Literatur
- D. G. Blackmond: Asymmetric Catalysis Special Feature Part II: Asymmetric autocatalysis and its implications for the origin of homochirality. In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 101, 2004, S. 5732. bibcode:2004PNAS..101.5732B. doi:10.1073/pnas.0308363101.
- Prof. Kenso Soai
- J. R. Islas: Mirror-symmetry breaking in the Soai reaction: A kinetic understanding. In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 102, 2005, S. 13743. bibcode:2005PNAS..10213743I. doi:10.1073/pnas.0503171102.
- KáRoly Micskei, Gyula Rábai, Emese Gál, Luciano Caglioti, Gyula Pályi: Oscillatory Symmetry Breaking in the Soai Reaction. In: The Journal of Physical Chemistry B. 112, Nr. 30, 2008, S. 9196. doi:10.1021/jp803334b. PMID 18593153.
- THE CONCEPT OF RACEMATES AND THE SOAI-REACTION. Abgerufen am 27. Dezember 2013.
- Joachim Podlech, Timo Gehring: New Aspects of Soai's Asymmetric Autocatalysis. In: Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 44, 2005, S. 5776. doi:10.1002/anie.200501742.
- Joachim Podlech, Timo Gehring: Fortschritte bei der asymmetrischen Autokatalyse nach Soai. In: Angewandte Chemie. 117, 2005, S. 5922. doi:10.1002/ange.200501742.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.