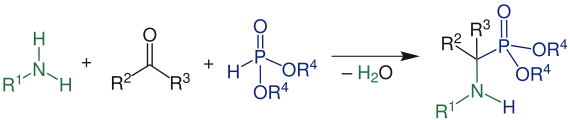
Kabachnik-Fields-Reaktion
Die Kabachnik-Fields-Reaktion ist eine Mehrkomponentenreaktion in der ein Aldehyd (R2= H, R3= H oder Organylgruppe), ein Amin (R1= H, Organylgruppe), und ein Phosphonsäurederivat ((R4=H, Organylgruppe), (R5=H, Organylgruppe)), zu einem α-Aminophosphonat umgesetzt werden. Die Reaktion wurde 1952 unabhängig voneinander von Martin Israilewitsch Kabachnik[1] und Ellis K. Fields[2] entdeckt.
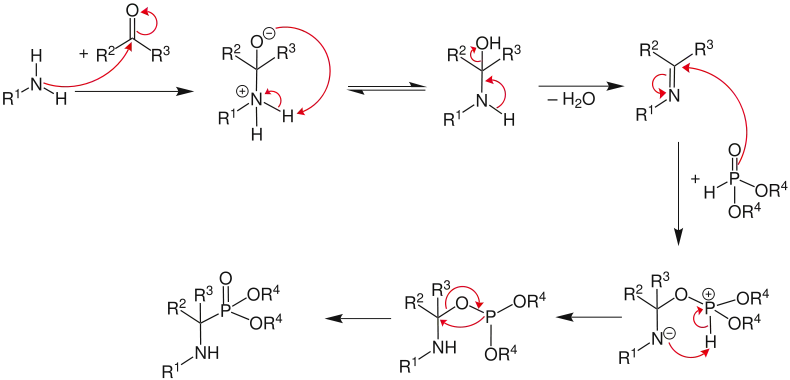
Mechanismus
Im ersten Schritt greift das Amin den Aldehyd am Carbonylkohlenstoffatom an. Dabei entsteht ein Zwitterion, welches durch Umlagerung eines Wasserstoffatoms (Tautomerie) und anschließender Abspaltung von Wasser zum Imin reagiert. Im nächsten Schritt addiert sich das Phosphonsäurederivat an das Imin. Nach einer weiteren Übertragung eines Wasserstoffatoms bildet sich letztlich das α-Aminophosphonat.[3]
Einzelnachweise
- Martin I. Kabachnik, T. Ya. Medved: Новый метод синтеза сс-аминофосфиновых кислот (A new method for the synthesis of α-amino phosphonic acids). In: Doklady Akademii Nauk SSSR. Band 83, 1952, S. 689.
- Ellis K. Fields: The synthesis of esters of substituted amino phosphonic acids. In: Journal of the American Chemical Society. Band 74, Nr. 6, 1952, S. 1528–1531, doi:10.1021/ja01126a054.
- Zerong Wang: Comprehensive Organic:Name Reactions and Reagents. Wiley Verlag, 2009, ISBN 978-0-471-70450-8, S. 1588–1591.