Fissura petrotympanica
Die Fissura petrotympanica – nach ihrem Erstbeschreiber Johann Heinrich Glaser[1] auch Glaser-Spalte – ist eine Öffnung der Schädelbasis, durch die die Chorda tympani (Paukensaite) und die Arteria tympanica anterior, ein Ast der Arteria maxillaris, hindurchtreten. Die Öffnung liegt zwischen der Pars petrosa (Felsenbein) und der Pars tympanica (Paukenteil) des Schläfenbeins (Os temporale) und dorsal der Fossa mandibularis, der Gelenkfläche des Kiefergelenks.
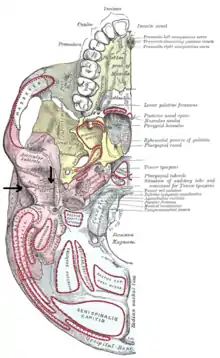
Fissura petrotympanica (mit Pfeilen gekennzeichnet), Blick von kaudal auf die Schädelbasis, In: Gray’s Anatomy, 20. Auflage, 1918
Anmerkungen
- Johann Heinrich Glaser: Tractatus de cerebro. Amsterdam 1680.
Literatur
- O. Eckerdal: The petrotympanic fissure: a link connecting the tympanic cavity and the temporomandibular joint. Cranio. 1991;9(1), S. 15–22. PMID 1843474
- M. Chiarini et al.: Permeability of the petrotympanic fissure. Journal of Oral Rehabilitation. 2002; Volume, Number 9, S. 885
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.