Vanillin-Synthase
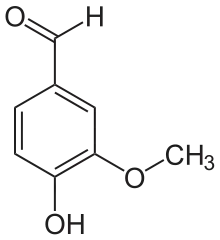
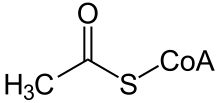
Die Vanillinsynthase (VS, EC 4.1.2.41) katalysiert die Spaltung von 3-Hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)propionyl-CoA in Vanillin und Acetyl-CoA.
propanoyl-CoA.svg.png.webp)
 +
+ 
| Vanillinsynthase | ||
|---|---|---|
| Bezeichner | ||
| Externe IDs |
| |
| Enzymklassifikation | ||
| EC, Kategorie | 4.1.2.41, Lyase | |
| Substrat | 3-Hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)propionyl-CoA | |
| Produkte | Vanillin, Acetyl-CoA | |
| Vorkommen | ||
| Übergeordnetes Taxon | Pseudomonas | |
Damit gehört das Enzym zu den Lyasen. Es wurde in manchen Pseudomonasstämmen und Streptomyces viridosporus[1] identifiziert.
Die durch die VS katalysierte Reaktion ist ein Zwischenschritt im Abbau von Ferulasäure zu Vanillin.[2] Vanillin wird dann durch eine weitere enzymatische Reaktion zu Protocatechusäure umgesetzt. Dieser Weg ist für den Ligninabbau von Bedeutung. Während Weißfäulepilze Lignin depolymerisieren, können bakterielle Mikroorganismen die entstandenen aromatischen Abbauprodukte weiter umsetzen.
Einzelnachweise
- A. L. Pometto 3rd, D. L. Crawford: Whole-cell bioconversion of vanillin to vanillic acid by Streptomyces viridosporus, in: Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1983, 45, S. 1582–1585; PMID 6870241.
- A. Narbad, M. J. Gasson: Metabolism of ferulic acid via vanillin using a novel CoA-dependent pathway in a newly-isolated strain of Pseudomonas fluorescens, in: Microbiology 1998, 144, S. 1397–1405; doi:10.1099/00221287-144-5-1397; PMID 9611814.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.