Phycocyanin
Phycocyanin (PC[1]) gehört zu den Phycobilinen und wirkt als akzessorisches Pigment der Photosynthese bei Cyanobakterien (Blaualgen), kommt aber auch bei Rotalgen und Glaucophyta vor. Farblich erscheint Phycocyanin purpurn bis kobaltblau.[2]
| Phycocyanin | ||
|---|---|---|
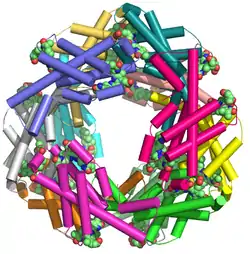 | ||
| Allophycocyanin 12-mer nach PDB 1all | ||
Sein Absorptionsmaximum liegt in Blaualgen (Aphanizomenon flos aquae) bei einer Wellenlänge von 615 nm. In verschiedenen Rotalgen ist sein Absorptionsspektrum zweigipfelig, mit Maxima jeweils um 550 nm und – stärker ausgeprägt – bei 615 nm.
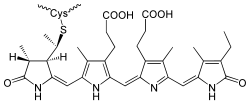
Die blaue chromophore Gruppe im Phycobilin ist das Phycocyanin. Es ist kovalent an das Proteinrückgrat des Phycobilin über ein L-Cystein verknüpft.[2]
Verwendung
Extrahiertes Phycocyanin ist ein blaues Pigment-Pulver, welches z. B. als Lebensmittelfarbstoff verwendet werden kann.[3]
Einzelnachweise
- Hans-Werner Heldt und Birgit Piechulla: Pflanzenbiochemie. Spektrum Akademischer Verlag; 4. Auflage 2008; ISBN 978-3-8274-1961-3; S. 63.
- Colyer, CL. et al. (2005): Analysis of cyanobacterial pigments and proteins by electrophoretic and chromatographic methods. In: Anal Bioanal Chem.382(3); 559–569; PMID 15714301; doi:10.1007/s00216-004-3020-4.
- Dinesh Kumar Saini, Hillol Chakdar, Sunil Pabbi, Pratyoosh Shukla: Enhancing production of microalgal biopigments through metabolic and genetic engineering. In: Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. Band 60, Nr. 3, 4. Februar 2020, ISSN 1040-8398, S. 391–405, doi:10.1080/10408398.2018.1533518 (tandfonline.com [abgerufen am 6. Januar 2021]).