Koilozyt
Koilozyten (gr. κοίλος, koilos = leer, konvex) sind infolge einer Infektion mit humanen Papillomviren (HPV) pathologisch veränderte Plattenepithelzellen, die morphologisch durch ein um den Zellkern gelegenes, scharf begrenztes optisch leeres Feld gekennzeichnet sind. Diese Zellen können weitere Veränderungen, wie eine Vergrößerung oder Schrumpfung (Pyknose) des Zellkerns, eine Doppel- oder Mehrkernigkeit oder ein vergröbertes und verstärkt anfärbbares (hyperchromatisches) Chromatin aufweisen.
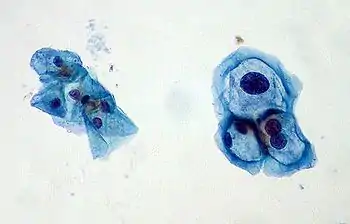
Zellabstrich aus dem Bereich des Muttermundes mit normalen Epithelzellen (links) und HPV-infizierten Epithelzellen (Koilozyten) auf der rechten Seite.
Das Auftreten von Koilozyten innerhalb eines Epithels wird auch als Koilozytose bezeichnet.
Literatur
- L. G. Koss, G. R. Durfee: Unusual patterns of squamous epithelium of the uterine cervix: cytologic and pathologic study of koilocytotic atypia. In: Ann N Y Acad Sci. 63, 1959, S. 1245–1247.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.