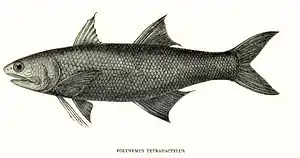
Fadenflosser
Die Fadenflosser (Polynemidae), auch Fingerfische genannt, sind eine Familie aus der Ordnung Carangiformes. Die ca. 40 Arten in acht Gattungen leben in tropischen und subtropischen Regionen weltweit im flachen küstennahen Meer und im Brackwasser, immer über sandigen und schlammigen Weichböden. Einige Arten wandern auch in Flüsse ein. Fünf Arten leben ausschließlich im Süßwasser.
| Fadenflosser | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
.jpg.webp)
Polydactylus octonemus | ||||||||||||
| Systematik | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
| Wissenschaftlicher Name | ||||||||||||
| Polynemidae | ||||||||||||
| Rafinesque, 1815 |
Merkmale
Ihren Namen haben die Tiere von ihren seltsamen Brustflossen, deren unterer Teil aus drei bis sieben fadenförmigen langen Strahlen besteht (14–15 bei Polynemus multifilis). Die Fadenflosser können mit Sinnesorganen auf diesen Fäden Beute aufspüren, wenn sie sie über den Boden schleifen lassen. Die Rückenflossen, eine hartstrahlige und eine weichstrahlige, sind durch eine Lücke deutlich voneinander getrennt. Die Bauchflossen befinden sich deutlich an der Körperunterseite, sie werden von einem Stachel und fünf verzweigten Flossenstrahlen gestützt. Die Schwanzflosse ist tief gegabelt. Fadenflosser besitzen 24 bis 25 Wirbel, das Maul ist unterständig. Sie werden elf Zentimeter bis zwei Meter lang.
Systematik
Es gibt acht Gattungen und über 40 Arten.
- Eleutheronema
- Eleutheronema rhadinum (Jordan & Evermann, 1902).
- Eleutheronema tetradactylum (Shaw, 1804).
- Eleutheronema tridactylum (Bleeker, 1849).
- Filimanus
 Filimanus heptadactyla
Filimanus heptadactyla- Filimanus heptadactyla (Cuvier, 1829).
- Filimanus hexanema (Cuvier, 1829).
- Filimanus perplexa Feltes, 1991.
- Filimanus sealei (Jordan & Richardson, 1910).
- Filimanus similis Feltes, 1991.
- Filimanus xanthonema (Valenciennes, 1831).
- Galeoides
- Galeoides decadactylus (Bloch, 1795).
- Leptomelanosoma
- Leptomelanosoma indicum (Shaw, 1804).
- Parapolynemus
- Parapolynemus verekeri (Saville-Kent, 1889).
- Pentanemus
 Pentanemus quinquarius
Pentanemus quinquarius- Pentanemus quinquarius (Linnaeus, 1758).
- Polydactylus
 Polydactylus plebeius
Polydactylus plebeius- Polydactylus approximans (Lay & Bennett, 1839).
- Polydactylus bifurcus Motomura, Kimura & Iwatsuki, 2001.
- Polydactylus longipes Motomura, Okamoto & Iwatsuki, 2001.
- Polydactylus macrochir (Günther, 1867).
- Polydactylus macrophthalmus (Bleeker, 1858).
- Polydactylus malagasyensis Motomura & Iwatsuki, 2001.
- Polydactylus microstomus (Bleeker, 1851).
- Polydactylus mullani (Hora, 1926).
- Polydactylus multiradiatus (Günther, 1860).
- Polydactylus nigripinnis Munro, 1964.
- Polydactylus octonemus (Girard, 1858).
- Polydactylus oligodon (Günther, 1860).
- Polydactylus opercularis Seale & Bean, 1907.
- Polydactylus persicus Motomura & Iwatsuki, 2001.
- Polydactylus plebeius (Broussonet, 1782).
- Fingerfisch (Polydactylus quadrifilis) (Cuvier, 1829).
- Polydactylus sexfilis (Valenciennes, 1831).
- Polydactylus sextarius (Bloch & Schneider, 1801).
- Polydactylus siamensis Motomura, Iwatsuki & Yoshino, 2001.
- Polydactylus virginicus (Linnaeus, 1758).
- Polynemus
- Polynemus aquilonaris Motomura, 2003.
- Polynemus bidentatus Motomura & Tsukawaki, 2006.
- Polynemus dubius Bleeker, 1854.
- Polynemus hornadayi Myers, 1936.
- Eleganter Paradies-Fadenfisch (Polynemus multifilis) Temminck & Schlegel, 1843.
- Polynemus paradiseus Linnaeus, 1758.
Polydactylus ist keine monophyletische Gattung, sondern ist mit allen anderen Fadenflossergattungen mit Ausnahme der basalen Gattung Pentanemus polyphyletisch tief verschachtelt. Monophyletisch ist nur eine kleine Gruppe um die Typusart Polydactylus virginicus zu der außerdem P. approximans, P. octonemus, P. oligodon und P. opercularis gehören.[1]
Literatur
- Joseph S. Nelson: Fishes of the World, John Wiley & Sons, 2006, ISBN 0-471-25031-7
- Roland J. McKay: Threadfins of the world (Family Polynemidae). An annotated and illustrated catalogue of polynemid species known to date. FAO Species Catalogue for Fishery Purposes. No. 3. FAO Rom 2004. (PDF)
- Matthew G. Girard, Matthew P. Davis, Carole C. Baldwin, Agnès Dettaï, Rene P. Martin und W. Leo Smith. 2022. Molecular Phylogeny of the Threadfin Fishes (Polynemidae) using Ultraconserved Elements. Journal of Fish Biology. DOI: 10.1111/jfb.14997
Einzelnachweise
- Matthew G. Girard, Matthew P. Davis, Carole C. Baldwin, Agnès Dettaï, Rene P. Martin und W. Leo Smith. 2022. Molecular Phylogeny of the Threadfin Fishes (Polynemidae) using Ultraconserved Elements. Journal of Fish Biology. DOI: 10.1111/jfb.14997
Weblinks
- Fadenflosser auf Fishbase.org (englisch)