Echelidai
Echelidai (altgriechisch Ἐχελίδαι) war ein antiker griechischer Ort in Attika. Er lag nahe der langen Mauern im Mündungsgebiet des Kephisos auf dem Gebiet des Demos Xypete.[1] Nach Stephanos von Byzanz war Echelidai ein Demos.[2]
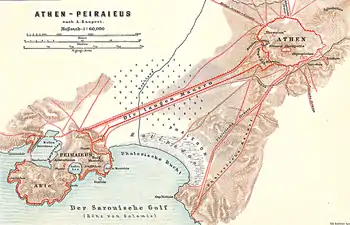
Mündungsgebiet des Kephisos zwischen den langen Mauern im Westen und den phalerischen Mauern im Osten
Echelidai wurde nach dem sumpfigen Boden (ἕλος, Sumpf) oder nach dem mythischen Heros Echelos (Ἔχελος) benannt.[2] Walther Judeich vermutete, dass sich das Hippodrom Athens hier befunden habe.[3]
Literatur
- Arthur Milchhoefer: Echelidai. In: Paulys Realencyclopädie der classischen Altertumswissenschaft (RE). Band V,2, Stuttgart 1905, Sp. 1911.
Einzelnachweise
- John S. Traill: The political organization of Attica. A study of the demes, trittyes, and phylai, and their representation in the Athenian Council. American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1975. S. 86 f.
- Stephanos von Byzanz: Ἔχελος
- Walther Judeich: Topographie von Athen. München 1905. S. 456.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.