Bohlmann-Rahtz-Synthese
Die Bohlmann-Rahtz-Synthese ist eine Namensreaktion in der Organischen Chemie. Die Reaktion ist nach ihren Entdeckern benannt, den deutschen Chemikern Ferdinand Bohlmann (1921–1991) und Dieter Rahtz (* 1925).
Dabei wird an einen 3-Aminocrotonsäureester (z. B. 1) entweder ein
- Alkinylalkylketon 2a addiert oder mit einem
- β-Diketon 2b unter Wasserabspaltung zum Zwischenprodukt 3 umgesetzt:
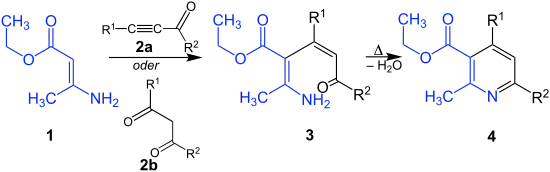
Bohlmann-Rahtz-Synthese
Die offenkettige Verbindung 3 cyclisiert beim Erwärmen unter Wasserabspaltung und Aromatisierung zu dem substituierten Ester 4 der Nicotinsäure.[1]
Weiterführende Literatur
- Christophe Allais, Jean-Marie Grassot, Jean Rodriguez, and Thierry Constantieux: Metal-Free Multicomponent Syntheses of Pyridines, Chemical Reviews (2014) 114, 10829–10868; dx.doi.org/10.1021/cr500099b
Einzelnachweise
- Theophil Eicher, Siegfried Hauptmann, Andreas Speicher: The Chemistry of Heterocycles, Wiley-VCH, 2012, ISBN 978-3-527-32747-8, S. 369.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. The authors of the article are listed here. Additional terms may apply for the media files, click on images to show image meta data.